Fiber Optics Geotechnical Instruments
For a much more detailed understanding of complex geomechanic phenomena in mining or civil projects, YieldPoint offers on a research and commercial basis the world’s highest resolution strain monitoring solution. This innovative geotechnical monitoring solution is based on Rayleigh backscatter of light along a single standard telecom optical fiber. Four years of intensive Research and Development have resulted in a combination of physical solutions and technical expertise that can be applied to the most complex problems in geomechanics. For example, YieldPoint is able to monitor the 3-D phenomena of shear deformation in rock, not only locating the exact depth of a shearing plane along a borehole in the rock but also determining the exact direction of that movement. YieldPoint can also accurately study multiple shear situations on systems several meters in length. 2 universities, one Canadian and one American, plus the Royal Military College and a large tunnel project in Australia have already taken advantage of this unique and progressive technology.
The standard optical products that YieldPoint has developed can be divided into three application categories:
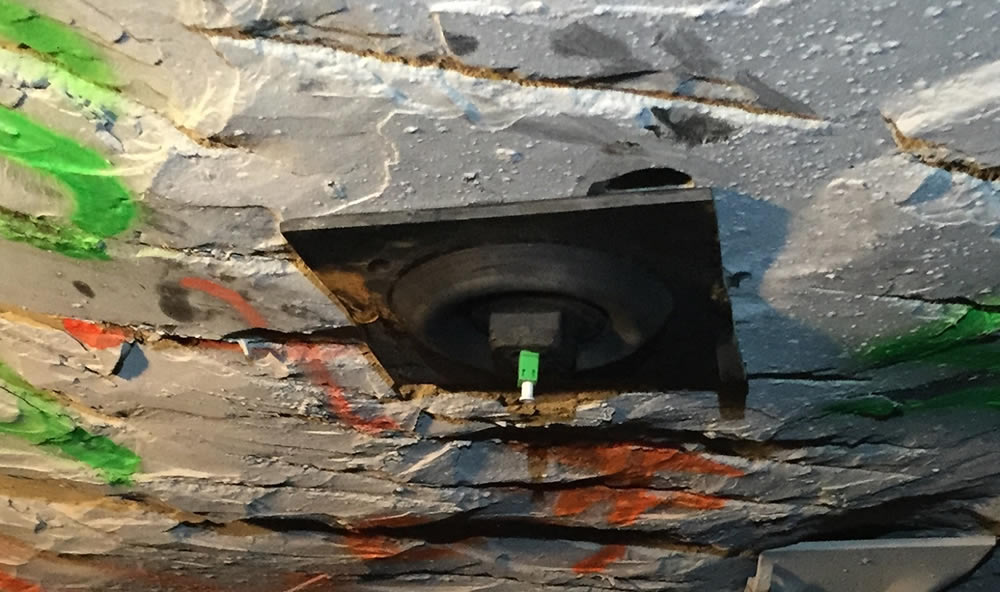
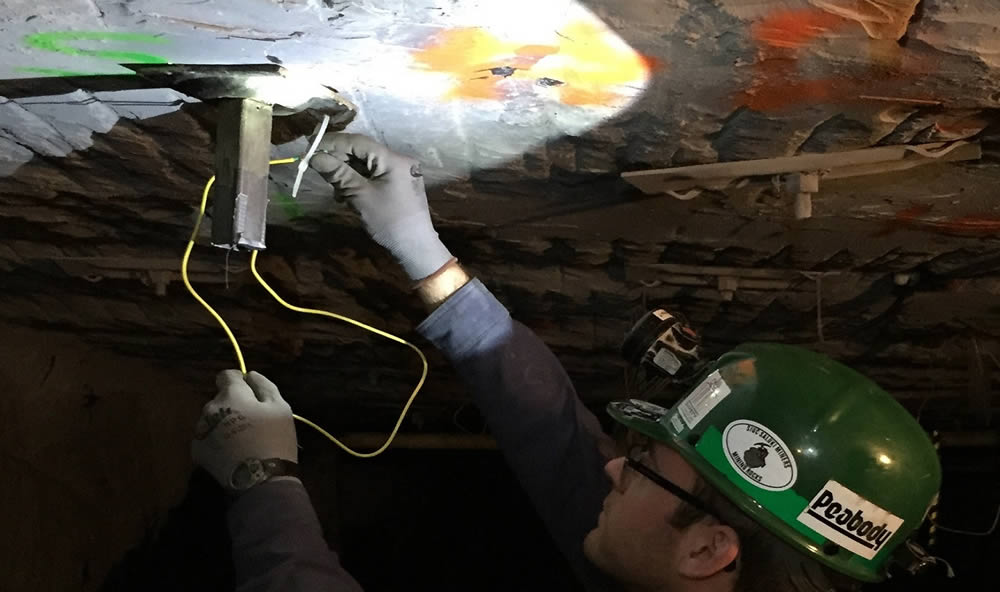
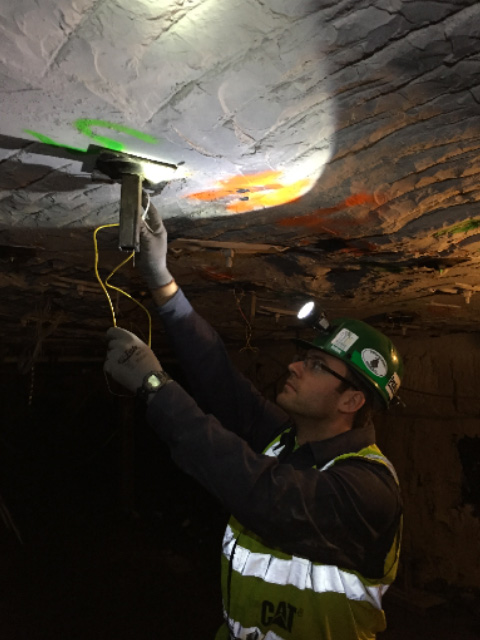
Optical rock Bolts: Rock Bolt monitoring in a US Coal Mine
YieldPoint is the world leader in high resolution Distributed Optical Sensing (DOS) for geotechnical monitoring. Brad Forbes has developed this technology during his MASc and Ph.D. research under the supervision of Prof N. Vlachopoulos and Prof. M Deiderichs.
Bolts can be fitted with Optical fibers in either two or three groves along the bolt length. If three grooves are used the detailed shape of the bolt can be determined as it loaded by ground movements. The axial “stretch” and lateral “shear” of the bolt can be resolved, making this the only technology that can monitor the latter. By running the optical fiber along 3 grooves in the 3D deformed shape of the bolt can be determined. This capability has been used for monitoring the NorthConnex road tunnel in Sydney Australia. Currently, the technology is being used to measure the deformation of spiles for a the TransEd LRT line in Edmonton AB.
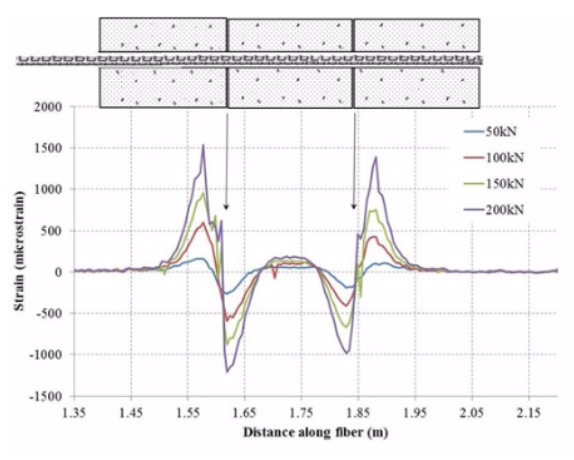
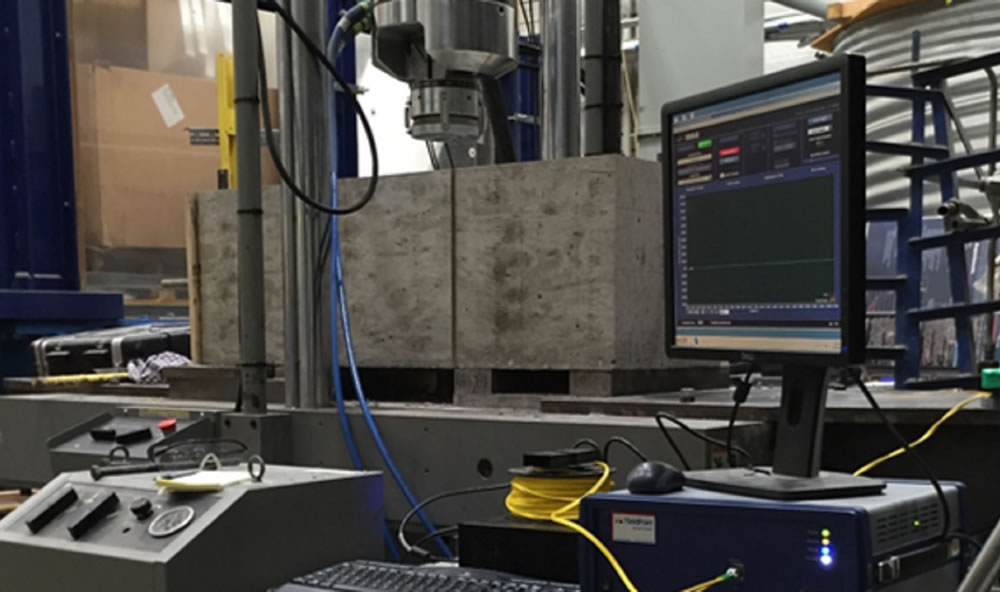
The distribution of axial strain during a double shear test
Prof. Doug Milne at the University of Saskatchewan is using DOS technology to conduct monitoring of rebar in Potash mines. The UofS team have been installing optical reabars into underground potash mines where they expect the bolts to be subjected to interbed shearing.

An optical rebar installed in a US coal mine.
Research services
Our research has been supported by Prof. Sam Spearing at Southern Illinois University at Carbondale and Prof. Nick Vlachopoulos, at the Royal Military College of Canada and Queen’s University. The research team is grateful for the assistance of both institutions. Several presented papers are provided here.




